The Federal Nuclear Science and Technology Work Plan performs nuclear-related science and technology (S&T) to support core federal roles, responsibilities and priorities, while maintaining necessary capabilities and expertise at Canadian Nuclear Laboratories (CNL). This represents an annual investment of $76 million.
The Federal Nuclear Science and Technology Work Plan serves the collective interests of 14 federal departments and agencies in the areas of health, nuclear safety and security, energy and the environment.
AECL is responsible for the management and oversight of the Federal Nuclear Science and Technology Work Plan and engages with the various federal departments and agencies to develop a program of work that meets their needs and priorities and to oversee the delivery of the work to bring value for money for Canada.
The program of work in the Federal Nuclear Science and Technology Work Plan is governed by an Interdepartmental Steering Committee, an Interdepartmental Integration Committee, and five Research Theme Sub-Committees (Sub-committees) with AECL as the program administrator and oversight organization.
The objective is to leverage the vast experience and expertise at the Chalk River Laboratories – Canada’s largest science and technology complex – to contribute to the government’s health, science, innovation and climate change objectives.
The Federal Nuclear Science and Technology Work Plan focuses on four research themes and activities:
- Supporting the development of biological applications and understanding the implications of radiation on living things. Learn more about Health and Biological Applications >>
- Supporting environmental stewardship and radioactive waste management. Learn more about Environmental Stewardship and Radioactive Waste Management >>
- Enhancing national and global security, nuclear preparedness and emergency response. Learn more about National Security & Emergency Preparedness >>
- Supporting safe, secure and responsible use and development of nuclear technologies. Learn more about New Nuclear Technologies >>
Governance Structure
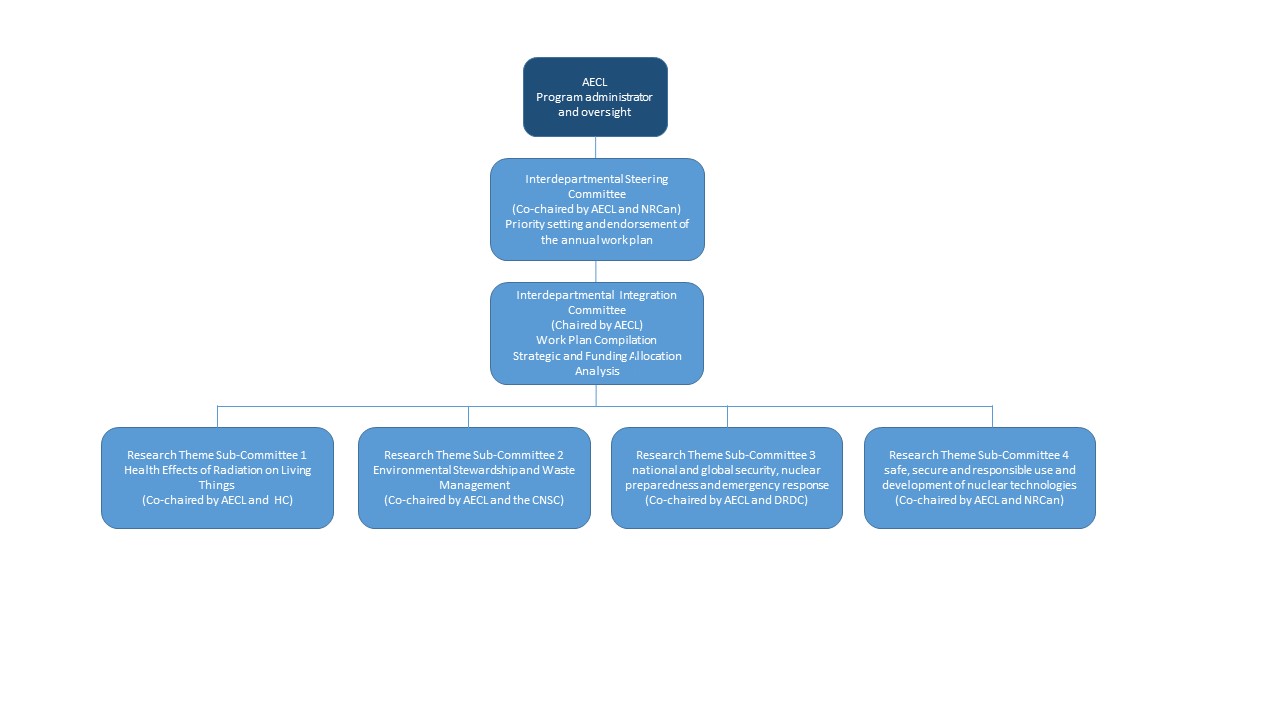
Description of the above diagram Governance Structure of AECL
- AECL : Program Administrator and oversight
- Interdepartmental Steering Committee (Co-chaired by AECL and NRCan) Priority setting and endorsement of the annual work plan
- Interdepartmental Integration Committee (Chaired by AECL) Work plan compilation Strategic and funding allocation analysis
- Research Theme Sub-Committee 1
Health Effects of Radiation on Living Things (Co-chaired by AECL and Health Canada) - Research Theme Sub-Committee 2
Environmental Stewardship and Waste Management(Co-chaired by AECL and the CNSC) - Research Theme Sub-Committee 3
National and global security, nuclear preparedness and emergency response (Co-chaired by AECL and DRDC) - Research Theme Sub-Committee 4
Safe, secure and responsible use and development of nuclear technologies (Co-chaired by AECL and NRCan)
- Research Theme Sub-Committee 1
For example, activities to support these research themes include:
Research to support the potential development of small modular reactors in Canada.
Small modular reactors are meant to be smaller, simpler and safer. They could potentially provide low-carbon energy to the mining and gas industry and remote communities, or be used in existing electrified areas to help meet increased electricity demand (due in part to the rise of electric vehicles). As a non-greenhouse gas emitting source of energy, small modular reactors could help Canada meet its commitments to reducing its carbon footprint.
Research on alpha-emitting isotopes for health applications.
Alpha-emitting isotopes are a promising new area for cancer treatment, whereby we could more effectively fight cancer and other diseases by targeting treatments directly to tumors and limiting the damage to surrounding areas of the body.
Protecting industrial control systems used in nuclear power plants and other critical energy infrastructure from cyber-security risks and threats.
This includes developing an anomalous detection software for monitoring, detecting and mitigating cyber-intrusion and cyber-physical security events in complex real-time systems and associated communication networks.
Advancing capability in nuclear detection, forensics and response
For example, technologies and methodologies to help detect illicit (illegal) nuclear materials.
Work in materials degradation for existing and next-generation reactors in Canada to inform regulation.
By better understanding the behavior of materials, particularly materials exposed to high levels of radiation inside nuclear reactors, we can provide risk-informed, science-based evidence, for regulatory decision making so reactors continue to operate safely.
Research to support the understanding of the effects of radiation on the environment
Improving the understanding of the migration of radioisotopes in the environment, and their potential impacts on human health and non-human biota.


